Jiangsu Jinling Drying
841939990
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
| Quantity: | |
Product Description
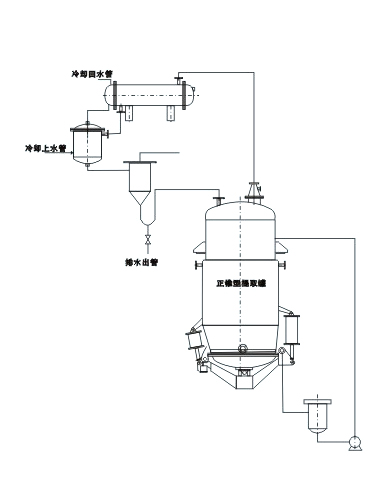
The extracting tank is a highly versatile and essential piece of equipment widely used in industries such as traditional Chinese medicine, food production, and the chemical sector. Its design and functionality allow it to perform a variety of extraction processes under different operating conditions. Whether it’s used for water decoction, warm dipping, hot reflux, or more advanced processes like the recovery of organic solvents, the extracting tank meets the diverse needs of modern industrial applications.
This equipment is engineered with the flexibility to adapt to numerous scenarios, making it a critical tool for industries that rely on the efficient extraction of active ingredients, aromatic oils, or other valuable components from raw materials. Its ability to perform under both atmospheric pressure and micro-pressure further enhances its utility, providing businesses with a reliable and efficient solution for their extraction needs.
The tank can function under both atmospheric pressure and micro-pressure conditions, giving it the flexibility to handle different types of materials and extraction requirements. Atmospheric pressure is typically used for straightforward processes, while micro-pressure is ideal for more delicate or controlled extractions.
Water decoction is a common method used in traditional Chinese medicine to extract active ingredients from herbs. The extracting tank is highly efficient in performing this process, ensuring that the valuable components are extracted while maintaining their integrity.
Warm dipping involves soaking raw materials in a warm solvent to extract soluble components, while hot reflux employs heat and solvent circulation for maximum efficiency. The extracting tank is optimized for both methods, ensuring consistent and high-quality results.
Forced circulation involves the continuous movement of the extraction solvent through the raw materials, while percolation allows the solvent to pass through the materials slowly to extract specific compounds. The extracting tank’s design supports these techniques, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
In the traditional Chinese medicine industry, the extracting tank plays a crucial role in the preparation of herbal remedies. It is commonly used for:
Water Decoction: Extracting active compounds from herbs through boiling in water.
Hot Reflux Extraction: Enhancing the yield of active ingredients by using heat and solvent circulation.
Percolation: Allowing the precise extraction of specific compounds from raw materials.
The ability of the extracting tank to perform these processes efficiently ensures that the final products retain their therapeutic properties, meeting the high standards required in this industry.
The extracting tank is also widely used in the food industry for extracting flavors, aromas, and nutrients. Applications include:
Aromatic Oil Extraction: Extracting essential oils from plants such as citrus, lavender, or mint for use in food flavoring.
Nutrient Extraction: Obtaining vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients from natural sources to fortify food products.
These capabilities make the extracting tank an indispensable tool for companies focused on producing high-quality food products with natural ingredients.
In the chemical industry, the extracting tank is used for a variety of purposes, including:
Organic Solvent Recovery: Recovering and reusing organic solvents during the extraction process, which reduces waste and lowers costs.
Forced Circulation and Percolation: Extracting valuable compounds from raw materials for use in chemical formulations or products.
The tank’s ability to handle complex chemical extractions and recover solvents makes it a cost-effective solution for chemical manufacturers.
The hot reflux system integrated into the extracting tank allows for efficient heat transfer and solvent recycling, making it possible to achieve maximum extraction yields. By continuously circulating the heated solvent through the raw materials, the tank ensures that every valuable compound is extracted efficiently.
The forced circulation system enhances the extraction process by moving the solvent through the materials at a controlled rate. This method is particularly useful for large-scale operations, as it reduces processing time and increases overall efficiency.
A standout feature of the extracting tank is its ability to recover organic solvents during the extraction process. This not only reduces waste but also minimizes the environmental impact of industrial operations. The recovered solvents can be reused, lowering production costs and improving sustainability.
Versatility: The tank’s ability to perform various extraction methods, such as water decoction, warm dipping, and hot reflux, makes it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Efficiency: Advanced systems like forced circulation and hot reflux ensure that the extraction process is both thorough and fast, maximizing yield.
Sustainability: The recovery of organic solvents reduces waste and promotes environmentally friendly practices.
High Quality: By maintaining precise control over pressure, temperature, and solvent circulation, the tank ensures that the extracted compounds retain their desired properties.
The extracting tank is an indispensable tool for industries that rely on efficient and high-quality extraction processes. Its ability to operate under diverse conditions, such as atmospheric pressure, micro-pressure, water decoction, and hot reflux, makes it a versatile solution for extracting valuable components from raw materials.
Whether it’s being used in the traditional Chinese medicine industry to prepare herbal remedies, in the food industry to extract flavors and nutrients, or in the chemical sector for solvent recovery and compound extraction, the extracting tank consistently delivers excellent results. Its advanced features, including forced circulation systems and solvent recovery capabilities, further enhance its efficiency and sustainability.
For businesses looking to optimize their extraction processes, the extracting tank is a reliable and cost-effective choice that meets the demands of modern production.
Model | TQ-0.5 | TQ-1 | TQ-2 | TQ-3 | TQ-4 | TQ-6 | TQ-8 | TQ-10 |
Volume | 600 | 1200 | 2300 | 3200 | 4300 | 6300 | 8500 | 11000 |
Design Pressure Inside the Tank | 0.09 | |||||||
Design Pressure Inside the Jacket | 0.3 | |||||||
Diameter of Feed Port (mm) | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 500 | 500 | 500 | 600 |
Heating Area (m2) | 2.4 | 3 | 4.7 | 6.8 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 13 |
Condensing Area(m2) | 3 | 4 | 5.4 | 8 | 14 | 18 | 22 | 24 |
Cooling Area(m2) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
Filtering Area(m2) | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
Diameter of Residuals Discharge Port (mm) | 600 | 800 | 800 | 1000 | 1000 | 1200 | 1400 | 1500 |
Steam Consumption (t/h) | 285 | 285 | 346 | 570 | 660 | 718 | 903 | 1140 |
Water Consumption (t/h) | 2.1 | 2.1 | 2.5 | 4.2 | 4.5 | 5.5 | 6.7 | 6.7 |
Electric Power (kW) | 2.2 | 2.2 | 3 | 4 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 7.5 | 7.5 |
Stirring Speed (r/min) | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 | 36 |
Pre-service
Act as a good adviser and assistant of clients to enable them get rich and generous returns on their investments.
1. Introduce the product to the customer in detail, answer the question raised by customer carefully;
2.Make plans for choice according to the needs and special requirements of users in different sectors;
Sale service
1. Ensure product with high quality and pre-commissioning before delivery;
2. Delivery on time;
3.Provide full set of documents meet customer’s requirements.
After-sale service
Provide considerate services to minimize clients’ worries.
1.Assist clients to prepare for the first construction scheme;
2.Install and debug the equipment;
3.Train the first-line operators;
4. Examine the equipment;
5.Take initiative to eliminate the troubles rapidly;
6.Provide technical support;
7.Establish long-term and friendly relationship.
Service commitment
1. Provide clients one-year warranty to make sure the machine work well;
2.We always keep certain inventory level of spare parts, which means the replacements can be sent to you
Jiangsu Jinling Drying Technology Co., Ltd. was founded in 2000, as an innovation-oriented enterprise specialized in advanced technology.We have over 30 years of experience in machine manufacturing. We have achieved more than fifty national level patents and ten provincial level certificates for new high-tech products. There are more than 120 employees in our factory, Jinling is professionally engaged in designing, manufacturing over 30 series of drying equipment, environmental protection equipment, evaporation & concentration equipment and dry granulation equipment which are widely used for environmental protection field, chemical field, food field, national defense field etc.
Jinling is the qualified manufacturer of special pressure vessel, established the biggest drying & granulating testcenter in China, and passed the examination of ISO 9001, ISO 14001, OHSAS18001 and CE certification.Jinling's equipment has been spread all over China and has been exported to over 40 countries.


1. Q: Jiangsu Jinling Drying Technology Co., Ltd is a manufacturer, trading company or a third party?
A: We are a manufacturer, Our company established in 2000.
2. Q: Where is your factory located?
A: Jinling is located in Changzhou city, Jiansu province, China. it is In the middle of Shanghai and Nanjing.
3. Q: How can I go to your factory?
A: You can fly to shanghai Pudong or Hongqiao international airport directly, then take the high speed train to Changzhou station (just 1 hour from Shanghai to Changzhou by train) and we arrange to pick you up at Changzhou station to go to our company. Yutong company is around 30km away from Changzhou station.
If you are in China now, you can fly to Changzhou Benniu airport, or take train or bus to Changzhou city directly .
We sincerely welcome to visit our company at any time.